First steps
The very basic tutorials to get a first impression of and some orientation in GroIMP. Additionally: Use the GroIMP software (video tutorials)
Running your first Model
This tutorial start from an installed setup yith GroIMP and has a look around the Window and the first simulation to get an Idea what all the buttons do.
RGG Code structure introduction
The RGG programming language repents the core of almost all GroIMP models. It is used to describe the simulation and analysis of the models and can be quite overwhelming at first. This tutorial describes the basic concept and the structure of a simple simulation.
GUI introduction
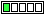
GroIMP is equipped with a modern, configurable graphical user interface. It supports user-defined layouts of panels, including arrangement of panels in tab groups and floating windows. Figure 2.1, “Screenshot of GroIMP” shows a typical screenshot with 3D view.
Figure 2.1. Screenshot of GroIMP
You can see the panels View, Attribute Editor, File Explorer, Text Editor, Toolbar and Statusbar. The panels Images and Materials are hidden, they are arranged together with File Explorer in a tab group. The panel Text Editor is not contained in GroIMP's main window but in its own floating window. Details of these panels will be described in the following.
Project handling
The main entity you work on in GroIMP is the project. A project may consist of various parts, e.g., files, source code, a scene (2D, 3D, or other), resource objects like data sets, 3D materials or the like. Several projects can be open at the same time, each in its own main window.
Import objects
GroIMP can import objects from several 3d or graph formats into the project graph. The imported objects can then be used similar to any other part of the graph.
In the following different way of adding a file will be shown based on this dtd file.